
BMC Genomic Data: De novo genome assembly and analysis unveil biosynthetic and metabolic potentials of Pseudomonas fragi A13BB
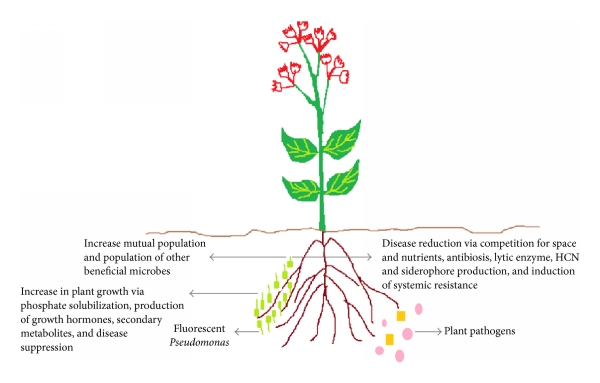
Pseudomonas fragi A13BB, recovered as part of study to identify novel antibiotic-producing bacterial strains from soil samples collected from the rhizosphere, has been sequenced for antibiotic producing gene clusters and has been published as the first Data Note in BMC Genomic Data. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are one of the components of the rhizosphere, where they promote plant growth by enhancing uptake of nutrients, inorganic elements, or by increasing resistance to heavy metals, high salt concentrations, phytopathogens and more.
Two β-lactone secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters (smBGC) known for their antibiotic, antiobesity and anticancer properties, were identified and demonstrated low homology (20%) to known smBGCs. A siderophore (a small compound secreted usually to transfer iron across cell membranes) smBGC was identified even though P. fragi is considered a non-siderophore producing member of the genus Pseudomonas.
BMC Nutrition: Did imports of sweetened beverages to Pacific Island countries increase between 2000 and 2015?

This study was intended to identify trends in the variety and amount of imported sweetened beverages (SB) to Pacific Island countries (and the impact of the SB taxes on imports in Fiji and Tonga). A major cause of death and sickness in these countries is nutrition-related chronic diseases.
The authors found there was an increase in SB imports into pacific island countries between these dates which needs to be considered for health implications by both exporting and importing countries as this has a detrimental impact on diet and self-sufficiency. Diet high in processed foods is well known to have an impact on health. There was a statistically significant increase in SB imports to Tonga but too little data for assessment of taxes.
BMC Psychiatry: A qualitative study of experiences of NHS mental healthcare workers during the Covid-19 pandemic

Thirty five members of NHS secondary mental health services (England) undertook an interview based study and were found to face difficulties that impacted significantly on their well-being during the pandemic.
The lockdown in England in response to the pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-19 had impact on all Healthcare workers but that on the mental Healthcare workers has been under-reported. The quality of life for respondents was affected by their challenge of providing care in constrained and potentially dangerous situations and losing patients to the disease. Taking on additional tasks to provide a better service for their patients led to additional strain. Feelings of grief, helplessness, isolation, distress, and burnout were all reported. The response to the pandemic meant that services had to rapidly adapt to major incident mode at the same time as the needs of service users increased. Moral injury has resulted to some after exposure to this event.
This study has pointed to areas where additional support could be targeted. One Implication is loss of staff but this has not been explicitly stated.
BMC Medical Ethics: Cultures and cures: neurodiversity and brain organoids
Cells from donors with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can now be grown into brain organoids and the resulting research is opening up our understanding of the aetiology of ASD. Brain organoids are allowing the exploration into genetic, developmental and other factors involved which makes this unique from other forms of research. Researchers often incorporate the medical model of disability into ASD research.
The neurodiversity movement is likely to disagree with approaches and aims of cerebral research in ASD as the developmental disability movement and paradigm understands autism as a form of human diversity and advocates a model based on social, attitudinal, and environmental barriers rather than any deficits.
The authors give three recommendations that should minimise any conflict and achieve a more holistic, inclusive approach to cerebral organoid research on ASD.
1 – neurodiverse individuals should be included as co-creators in both the scientific process and research communication.
2 – clinicians and neurodiverse communities should have open and respectful communication.
3 – a continual reconceptualization of illness, impairment, disability, behavior, and person should be achieved.
Researchers are advised to be careful not to combine disease with impairment or disability and also consider how best to communicate their ideas with respect and care.
BMC Endocrine Disorders: The effects of vitamin and mineral supplementation on women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as impaired glucose tolerance with onset or first recognized during pregnancy. It is fairly prevalent with a figure of 15-20% reported globally. Hyperglycaemia is associated with adverse outcomes for mother and baby.
Vitamin and mineral supplementation such as vitamin D, vitamin E, magnesium, and selenium may regulate glucose metabolism and have beneficial roles in anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress.; does it help in GDM? The effects of vitamin and mineral supplementation on women with GDM have not been well established but this meta-analysis hoped to rectify that.
The Authors’ findings are that vitamin and mineral supplementation; magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, vitamin D and E (alone or in combination), significantly improved glycemic control, lessened inflammation and oxidative stress in women with GDM through decreasing serum Fasting Plasma Glucose, insulin, and other levels, and increasing total antioxidant capacity levels.
Comments