

Common mental health disorders, or CMDs, such as anxiety, depression and stress significantly contribute to workplace absences. Intervention programmes have been employed in workplaces to aid people with a history of or presently experiencing mental health issues but present some limitations, among which is the identification of staff experiencing CMDs.
Prevail is presented as a new intervention strategy that focuses instead on the whole workforce, aiming to increase the overall mental wellbeing of employees. The aims of the new programme include reducing the stigma of mental health, increasing the level of awareness of mental health issues, educating staff to manage mental health issues within the workplace and encouraging people to disclose potential issues they are experiencing.
In this study, the delivery of the Prevail intervention was very well received, with 81% of the participants stating it was helpful in improving their own mental health. While there was no distinct effect on the level of stigma towards others, evidence suggests that the Prevail intervention is successful in reducing self- and anticipated stigma and social distance from people with mental health issues. In addition, a reduction in levels of sickness absence was observed between the pre- and post-intervention periods.
This study presents a novel approach to tackling common mental health disorders in the work environment by addressing the whole workforce and shows its effectiveness in improving their overall mental wellbeing.
BMC Ecology and Evolution – A late-surviving phytosaur from the northern Atlantic rift reveals climate constraints on Triassic reptile biogeography
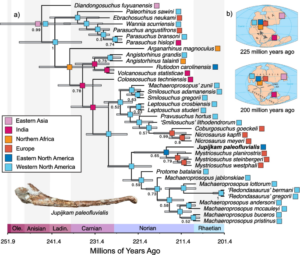
The Triassic period (252-201 million years ago) separates the Permian and the Jurassic Periods and marks the start of the Mesozoic Era. It followed the most devastating mass extinction event in history. This Period was characterised by the expansion and diversification of reptiles and saw the first appearance of dinosaurs, belonging to the Archosauria.
Phytosaurs, also archosauromorphs, were mostly semi-aquatic reptiles and fossil record allowed to determine they were spread across the Pangea. In this study, phylogenetic analysis allowed to determine that a partial skull and bone fragments collected in 1974 in Nova Scotia, Canada belong to a new phytosaur genus and species, named Jupijkam paleofluvialis. The biogeographic reconstructions show that this new species is one of the youngest phytosaur lineage to have been identified.
Phylogenetic analysis also allowed to infer that climate events, in particular related to an arid central belt, were important determinants not only in the spreading of phytosaurs, but in establishing the biogeography of vertebrates in the Triassic Period.
This article is part of the ‘Paleoecology of extinct species’ Collection, currently open for submissions. You can read more about the Collection here: https://www.biomedcentral.com/collections/POES
BMC Medical Research Methodology – Estimating medication adherence from Electronic Health Records: comparing methods for mining and processing asthma treatment prescriptions

Medication adherence is a key determinant of treatment success. Additional, unnecessary treatment may be needed as a consequence of non-adherence, leading to increased patient discomfort as well as financial costs. Being able to efficiently estimate adherence means also being able to determine the associated costs and identify patients most at risk of non-adherence.
Data mining of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is an opportunity to expand adherence estimation to large scale groups, but consensus on the best method to do so is lacking.
This study compared different adherence measures using a Scottish EHR dataset for asthma medication. Of the eight Continuous, Multiple Interval, Measures of Medication Availability (CMAs) that were assessed, CMAs 1 to 4 calculate the amount of medication obtained over a certain period, while CMAs 5 to 8 are based on the timing of the prescriptions. In the context of the study, CMA7 and 8 proved reliable in estimating current adherence based on data from the previous year.
This study highlights key considerations to take into account when designing medication adherence estimates and provides a rule-based data extraction method which can be adapted to different conditions and regimens.
BMC Genomics – Chimeras in Merlot grapevine revealed by phase assembly

Merlot, a cross between Cabernet Franc and Magdeleine Noire des Charentes, is one of the most extensive wine cultivations in the world. Merlot, and grapevine in general, genome mapping and chimera identification can be helpful elements in selection and conservation efforts. Grapevine chimeras are an important element of viticulture and more specifically periclinical chimeras, where the somatic variation is present throughout the cell layer, are of particular interest due to their stability and their ability to be propagated through cuttings.
In this study, a method for genome sequencing and chimera identification is presented based on long reads sequencing, trio binning and organ comparison. A total of 51 and 53 chimeras originating from SNVs in non-repeated sequences were identified in Merlot Haplotype CF and Merlot Haplotype MG, respectively. Haplotype comparison yielded 3.5 million variants between Merlot-leaf-hap-MG or Merlot-root-hap-MG and Merlot-root-hap-CF pseudo-molecules – mostly Single Nucleotide Variants (SNVs).
These findings not only are significant for the cultivation of Merlot wine, but have a wider application for viticulture and plant breeding and conservation.
BMC Digital Health – End-user acceptability of a prototype digital stethoscope to diagnose childhood pneumonia- a qualitative exploration from Sylhet, Bangladesh

Low-income or resource-limited settings struggle to access adequate technologies to ensure a timely and accurate diagnosis of respiratory infections in children. Lack of resources impact the clinical training necessary for the operation of a standard stethoscope, making the assessment of symptoms challenging. A digital stethoscope prototype was developed to address such challenges, and in this study its usability and uptake were assessed in rural areas of Bangladesh.
The study involved both parents and community healthcare providers, aiming to identify the level of acceptance of the prototype use and its practical performance.
There was positive feedback on acceptance and the healthcare providers were happy with the level of training and support they received ahead of and during the enrolment. Issues were also reported, in relation to both the implementation and technological aspects. These included inability to charge the device due to lack of electricity, having to transport the device as such an expensive piece of kit cannot be stored in the clinic, and technical problems such as lack of visual cues and unwanted recording, which also raises privacy concerns.
This study provides valuable feedback on practical aspects of the implementation of digital devices in resource-limited settings and insights into areas with improvement potential.
Comments