Unsticking malaria
Recently published work suggests a toxin from the bacterium, Escherichia coli, could be a therapeutic tool for treatment of cerebral malaria.

Recently published work suggests a toxin from the bacterium, Escherichia coli, could be a therapeutic tool for treatment of cerebral malaria.
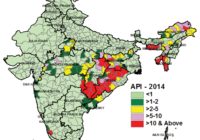
India has made huge strides towards malaria elimination but there is a long way to go. Successes and challenges are discussed here.

A new approach to the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis with magnetic nanobeads is showing promise.

New research uses high-speed videography and sound recordings to investigate the hidden world of mating in the yellow fever mosquito, revealing the importance of female choice and acoustic signalling in determining mating success.

A recent study by Coffeng and team uses mathematical model simulations to predict the short-term and long-term impact of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) interventions on soil-transmitted helminth control and elimination programmes. Their models demonstrate a clear added benefit of WASH interventions on sustaining the gains of preventative chemotherapy treatment (PCT), particularly after PCT is stopped, reducing the risk and speed of bounce-back of infections.

As research reveals the cause of a massive but neglected disease problem in sheep and goats, we ask – could this animal health problem be an early warning of a hidden human disease problem in Tanzania?

Krisztian Magori provides an update on the geographical distribution of the Asian longhorned tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis) in the United States, and his personal perspective getting involved in tracking this invasive tick.