
BMC Ecology and Evolution – Hadrosauroid eggs and embryos from the Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Jiangxi Province, China
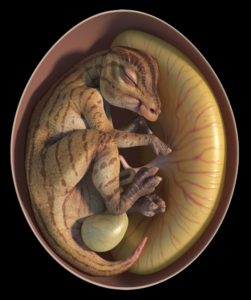
Were hadrosaurid hatchlings in need of extensive parental care? Although eggs from these dinosaurs are relatively common, they usually do not contain enough embryonic material to help define the early ontogeny of these large herbivores that lived near the end of the Age of Dinosaurs. In this recent BMC Ecology and Evolution publication, researchers from the University of Geosciences in China and the Carletown University in Canada studied two well preserved fossil embryos from an egg cluster found in the Upper Cretaceous red beds of the Ganzhou Basin in China and reached the conclusion that altriciality was probably the original ancestral condition for hadrosaurids. Although the embryos were yet several embryonic stages away from hatching, their limb bone structure indicated that the younglings of this small and primitive lineage of hadrosaurs were incapable of moving around on their own soon after hatching, having to spend some time in the nest until their limb bones finished forming.
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth – Isolation, marginalisation and disempowerment – understanding how interactions with health providers can influence smoking cessation in pregnancy
 There is enough robust evidence to say that smoking during pregnancy carries harmful effects, including an increased risk of miscarriage and placental abnormalities. Scientific studies also suggest that smoking cessation prior to 20 weeks of gestational age can eliminate that excess risk. However, socially disadvantaged pregnant women present lower success rates of tobacco discontinuation during pregnancy. In an effort to understand the barriers impeding antenatal smoking cessation in this population, researchers from the University of Adelaide conducted a series of interviews with 17 female smokers attending a metropolitan antenatal clinic in South Australia. Authors found that smoking was deeply embedded in these women’s socially disadvantaged lives. Quitting smoking was often a low priority as it was considered a necessary habit for coping with the challenges associated with their socioeconomic circumstances. These facts were the foundation of feelings of isolation, disempowerment, and marginalization around smoking from the general community, health service providers and sometimes their smoking social circle. The authors appeal to provide a more comprehensive health care approach able to cover the physiological, psychological, and sociological barriers to successful antenatal smoking cessation.
There is enough robust evidence to say that smoking during pregnancy carries harmful effects, including an increased risk of miscarriage and placental abnormalities. Scientific studies also suggest that smoking cessation prior to 20 weeks of gestational age can eliminate that excess risk. However, socially disadvantaged pregnant women present lower success rates of tobacco discontinuation during pregnancy. In an effort to understand the barriers impeding antenatal smoking cessation in this population, researchers from the University of Adelaide conducted a series of interviews with 17 female smokers attending a metropolitan antenatal clinic in South Australia. Authors found that smoking was deeply embedded in these women’s socially disadvantaged lives. Quitting smoking was often a low priority as it was considered a necessary habit for coping with the challenges associated with their socioeconomic circumstances. These facts were the foundation of feelings of isolation, disempowerment, and marginalization around smoking from the general community, health service providers and sometimes their smoking social circle. The authors appeal to provide a more comprehensive health care approach able to cover the physiological, psychological, and sociological barriers to successful antenatal smoking cessation.
 Genomic instability based on deficient DNA damage sensing and repair processes is an enabling trait during tumorigenesis. This characteristic has been exploited to establish DNA repair-targeting therapies in different cancer types, such as tumors where the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway is affected. In these cases, BCRA1/2 mutations have been classically used as a powerful tool for clinical risk assessment and management, but for patients without these mutations, the thresholds of genetic and epigenetic alterations able to trigger HRR deficiency phenotypes still need to be established. In their latest publication, Dr. Leivowitz and colleagues developed and validated a predictive diagnostic platform for assessing homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) in a wide number of cancer types. The authors combined an HRD-DNA approach, measuring genome-wide loss-of-heterozygosity with a HRD-RNA approach based on a logistic regression model trained on whole-exome capture RNA sequencing data. The model provides a gene expression HRD biomarker signature in different tumors, also detecting HRD driven by non-BRCA1/2 mechanisms. The study highlights how this approach may provide new biomarkers for HRD-status across different solid tumors with a lower frequency of biallelic BRCA loss.
Genomic instability based on deficient DNA damage sensing and repair processes is an enabling trait during tumorigenesis. This characteristic has been exploited to establish DNA repair-targeting therapies in different cancer types, such as tumors where the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway is affected. In these cases, BCRA1/2 mutations have been classically used as a powerful tool for clinical risk assessment and management, but for patients without these mutations, the thresholds of genetic and epigenetic alterations able to trigger HRR deficiency phenotypes still need to be established. In their latest publication, Dr. Leivowitz and colleagues developed and validated a predictive diagnostic platform for assessing homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) in a wide number of cancer types. The authors combined an HRD-DNA approach, measuring genome-wide loss-of-heterozygosity with a HRD-RNA approach based on a logistic regression model trained on whole-exome capture RNA sequencing data. The model provides a gene expression HRD biomarker signature in different tumors, also detecting HRD driven by non-BRCA1/2 mechanisms. The study highlights how this approach may provide new biomarkers for HRD-status across different solid tumors with a lower frequency of biallelic BRCA loss.
BMC Infectious Diseases – SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness against infection, symptomatic and severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 The value of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines as a public health strategy to manage the COVID-19 pandemic is a fact, but after the administration of 12 Billion dosages worldwide there is still a debate on the necessity and frequency of booster dosing. In their latest BMC Infectious Diseases publication, researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine and Milton S. Hershey Medical Center conducted a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials and cohort studies aimed to assess how immunity wanes over time after full COVID-19 vaccination. Using a pooled cohort of 7 million individuals followed up for months, the authors offer data on how vaccine efficiency against infection decreases from 83% to 22% after just five months, while the protection against symptomatic COVID-19 declines from 94% to 64% after four months. Positively, their results support a robust and persistent 90% protection against developing severe COVID-19 after full vaccination. The study concludes with a data-based recommendation of booster vaccination for individuals over 65 years old and those who received Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.
The value of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines as a public health strategy to manage the COVID-19 pandemic is a fact, but after the administration of 12 Billion dosages worldwide there is still a debate on the necessity and frequency of booster dosing. In their latest BMC Infectious Diseases publication, researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine and Milton S. Hershey Medical Center conducted a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials and cohort studies aimed to assess how immunity wanes over time after full COVID-19 vaccination. Using a pooled cohort of 7 million individuals followed up for months, the authors offer data on how vaccine efficiency against infection decreases from 83% to 22% after just five months, while the protection against symptomatic COVID-19 declines from 94% to 64% after four months. Positively, their results support a robust and persistent 90% protection against developing severe COVID-19 after full vaccination. The study concludes with a data-based recommendation of booster vaccination for individuals over 65 years old and those who received Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.
BMC Oral Health – Dentist perceptions about the value of teledentistry
 COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of virtual dental consultations, as teledentistry facilitates access to oral health care for patients without having to leave the safety of their homes. In their recent study, researchers from the University of Colorado and the CareQuest Institute for Oral Health in Boston explore dentist perceptions and barriers to the implementation of this technology. Although the authors state that previous studies have proven that teledentistry delivers similar or better outcomes than conventional healthcare while also being cost-effective, their results show that only 23% of the 2767 dental providers participating in the study use virtual platform consultations routinely. Among the reasons for not adopting teledentistry, the authors found that a considerable amount of practitioners are still concerned about the level of care delivered through virtual platforms. The authors conclude that there is a need to develop training programs, supportive legislation, and insurer regulations to help promote the uptake and suitability of the use of teledentistry.
COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of virtual dental consultations, as teledentistry facilitates access to oral health care for patients without having to leave the safety of their homes. In their recent study, researchers from the University of Colorado and the CareQuest Institute for Oral Health in Boston explore dentist perceptions and barriers to the implementation of this technology. Although the authors state that previous studies have proven that teledentistry delivers similar or better outcomes than conventional healthcare while also being cost-effective, their results show that only 23% of the 2767 dental providers participating in the study use virtual platform consultations routinely. Among the reasons for not adopting teledentistry, the authors found that a considerable amount of practitioners are still concerned about the level of care delivered through virtual platforms. The authors conclude that there is a need to develop training programs, supportive legislation, and insurer regulations to help promote the uptake and suitability of the use of teledentistry.
Comments