
The gallbladder is a pear shaped organ located within the abdomen of the human body. The primary function of the gallbladder is to store and concentrate the bile fluid produced by the human liver. Bile fluid plays an integral role in the digestion and absorption of fats from the human gut. However, due to its function as a bile concentrating organ, the gallbladder is also prone to develop gallstones. Gallstone disease is one of the commonest reasons why humans undergo a surgical intervention.
Cancer of the gallbladder is relatively rare in the western hemisphere.
Cancer of the gallbladder is relatively rare in the western hemisphere; however it is still the fifth commonest malignancy of the gastrointestinal tract. Annually, there are roughly 4000-5000 new cases of gallbladder cancer diagnosed in the United States. A vast majority of the gallbladder cancer cases are diagnosed in the advanced stages of disease (stage III and above) resulting in poor clinical outcomes.
The mean survival after a gallbladder cancer diagnosis is a mere six months. The five year survival (a metric to assess cancer outcomes) is less than 3-8% for stage III gallbladder cancer and above. It is one of the deadliest cancers we know of.
Gallbladder cancer incidence has a unique global distribution as well. Most of the cancers known to mankind tend to be relatively uniformly distributed across countries and continents. In contrast, gallbladder cancer incidence is increased in geographically distinct locations of the world. These include places such as Chile, Northern parts of India and the state of New Mexico in the United States. What are the common drivers unique to these locations leading to increased gallbladder cancer incidence? We do not know for sure at the present time.
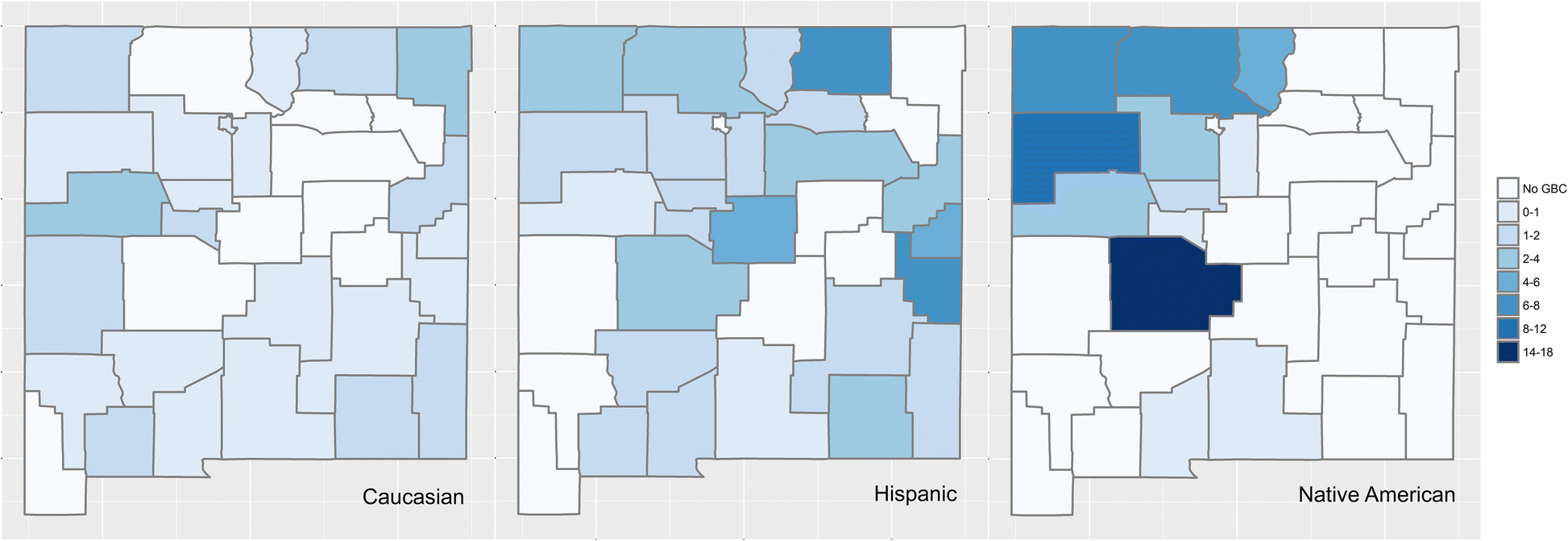
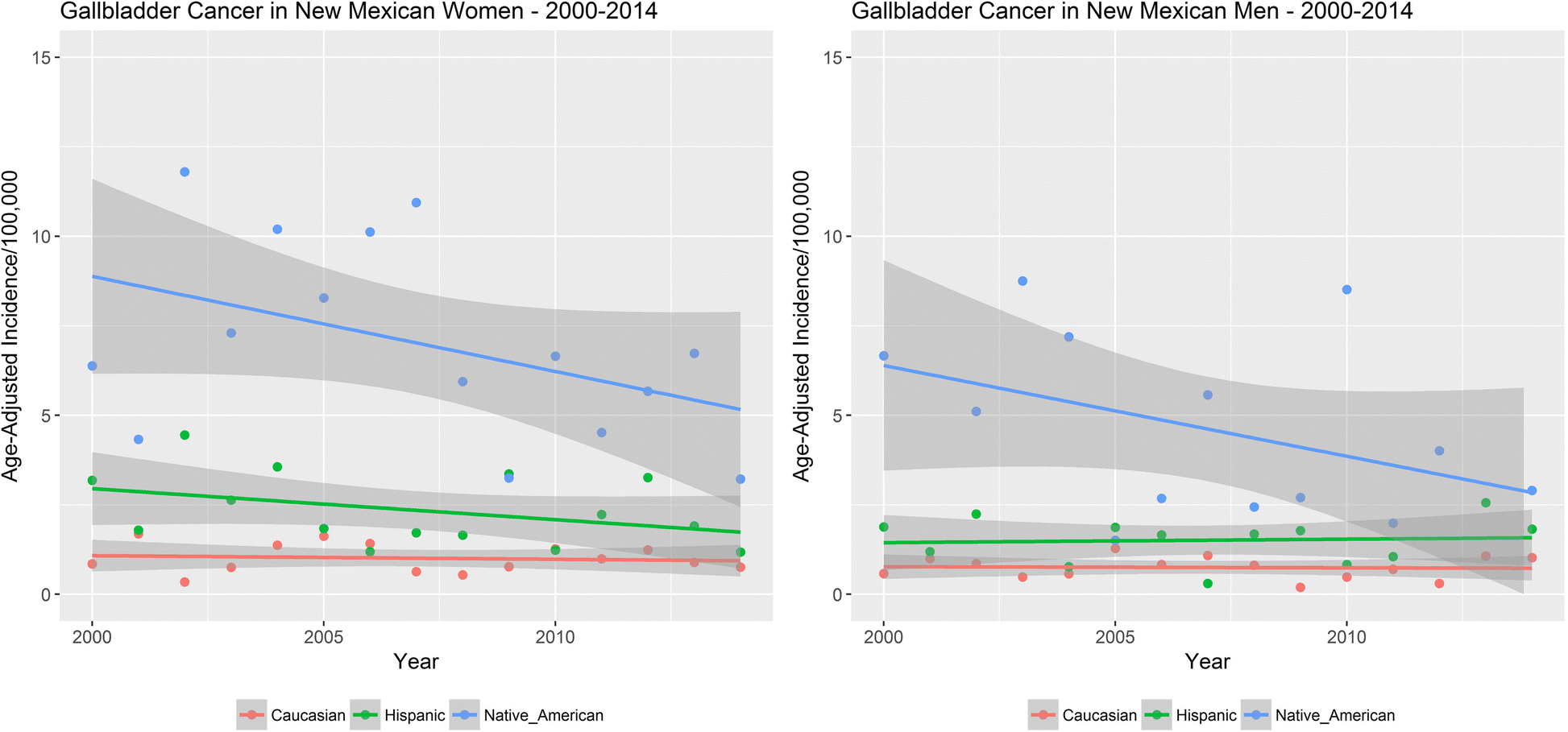
Native Americans in New Mexico have a five-fold elevated incidence of gallbladder cancer compared to the Caucasians within the state.
In addition to the unique geographical distribution, people of specific ethnicities appear to be more prone to gallbladder cancer as well. This includes the Native American populations of the North American continent. Native Americans in New Mexico have a five-fold elevated incidence of gallbladder cancer compared to the Caucasians within the state. While there are a multitude of risk factors that have been implicated in the causation of gallbladder cancer, there are no definitive associations. In our current review, we discuss these issues along with some likely factors implicated in the process of development of gallbladder cancers.
Another interesting feature is the elevated incidence of gallbladder cancer in women compared to men. Gallbladder cancer is one of the few cancers which has an elevated female incidence relative to men. Women are prone to develop gallstones in general. However, this does not explain the complete risk associated with increased gallbladder cancer development seen among women. Higher levels of estrogen may be one of the risk factors needed to drive gallbladder cancers and we need more research to understand its role in the development of this cancer.
A significant drawback in our understanding of gallbladder cancer is the lack of readily available cell line and animal models. Additionally, funding for gallbladder cancer research is very limited, impeding our understanding of this disease. In order to make a dent in this disease, global collaborative efforts are critically needed through pooled resources and improving the collective knowledge of this disease across institutions. Instances of such collaborative efforts include the Chile Gallbladder Cancer Pilot Study and the Shanghai Biliary Tract Cancer Study led by Dr Jill Koshiol at the NIH.
Finally, clinical therapeutic options in gallbladder cancers are quite limited for patients with this disease. With the new emerging focus on personalized medicine/oncology, research into targetable markers in gallbladder cancer patients is urgently required. Interestingly, gallbladder and biliary tract cancers appear to have an interesting array of potential molecular targets which may be amenable to targeted therapeutics. Clinical trials and basic research efforts are urgently needed to establish the validity of these approaches to move the translational research findings back to gallbladder cancer patients.
Clinical therapeutic options in gallbladder cancers are quite limited for patients with this disease.
Another issue which we highlight in our review is the issue related to rural oncology healthcare access. New Mexico is a predominantly rural state. Native Americans in the state live on reservations which are far-flung, lacking immediate access to oncology care. This means that the gallbladder cancer patients are often reluctant to travel far distances to obtain the necessary and appropriate care. One of the authors (UBG) is currently setting up a pilot clinical trial to enable tele-oncology based initiatives to address these issues.
In conclusion, our review paper highlights the major outstanding issues associated with gallbladder cancer. Due to the regional importance of this cancer within the state of New Mexico where both of us currently practice, we have sought to highlight the challenges surrounding gallbladder cancer in this review. There are currently far more questions than available answers surrounding this cancer. We are currently moving ahead with multiple initiatives (basic and clinical research) at our own institution (University of New Mexico Comprehensive Cancer Center) to make a dent in this rare, but deadly form of cancer.
One Comment