
BMC Rheumatology: New Journal Launch
We are pleased to announce the launch of the latest addition to the BMC series. BMC Rheumatology is now considering article submissions on all aspects of prevention, treatment and management of rheumatic diseases. To find out more, please read this blog post introducing the journal here.
BMC Plant Biology: Video of the month
A group of researchers from Italy have investigated how the environment can have a profound effect on the appearance, texture and flavor of tomato fruit.
To find out more, read the full article
BMC Zoology: Rediscovery of the African wolf
The African wolf (Canis lupaster) is a medium-sized canid with wolf-like characters. Because its appearance resembles that of the golden jackal, specimens have long been assigned to golden jackal. Viranta and colleagues have now carried out a taxonomic investigation of the African wolf. A skull and skin taxonomy assessment revealed that Canis lupaster is not a golden jackal at all, but rather a close relative of the Gray wolf. The authors provide a thorough species description through rigorous morphological analysis and assess its distribution in Africa. They have written a blog describing their study, which can be assessed here.
BMC Medical Ethics: Investigating the ethical issues of using smart-home health technologies
Interest in using smart-home technologies, that is, technologies that allow a user to control utilities and appliances remotely, is generally on the increase, including the home healthcare industry. Ethical considerations, such as privacy, user consent, risk of social isolation and equity of access have not, however, been extensively investigated. With this in mind, Birchley et al interviewed a number of researchers working for multi-center smart-home project and directly involved in the design and implementation of smart-home technologies. The researchers were asked to describe their own experiences of working on the project and their views on ethical considerations pertaining to the use smart-home technologies. Two ethical “themes” emerged, that of privacy and choice. Privacy concerns included possible unauthorized sharing of information and also “physical” privacy- in other words concerns about being watched or monitored. Choice focused on the challenge of balancing the end-user freedom to choose and ethical considerations that could limit these choices.
BMC Women’s Health: The pain experienced by amaXhosa women living with HIV/AIDS
Pain is one of the most common symptoms reported in people living with HIV/AIDS. Recent research suggests that, because many chronic pain conditions are more common in women than men, more women living with HIV/AIDS experience pain. In this study, Parker et al investigated chronic pain suffered by amaXhosa women living with HIV/AIDS and whether there were associations between pain in this population and various psychosocial factors, including employment, mental health issues and health-related quality of life. The researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 229 amaXhosa women registered for HIV/AIDS testing at a community health center. All participants were interviewed and asked to fill in a demographic questionnaire. Almost 75% of the women included reported experiencing a significant amount of pain and only two were receiving adequate pain management. Furthermore, pain was more prevalent in those women who were unemployed and had significantly fewer years of schooling; it was also had detrimental effects of mental health and health-related quality of life. The study concludes that pain is a common problem for amaXhosa women with HIV/AIDS and that routine pain assessments could help with the management of pain and mitigating much of its effects on people’s lives.
BMC Neuroscience: Is linoleic acid the key that unlocks the quantum brain?
Cocchi and colleagues published a review article discussing the role of linoleic acid on the functioning of the brain. In it they describe a mechanistic model that considers subneuronal structures in the brain, such as ion channels, membrane fatty acids and the cytoskeleton, as part of a finely balanced dynamic system that are vital to a healthy brain. Subtle membrane fatty acid changes can disrupt this balance, causing, for example dysregulation of the membrane, cytoskeleton and their interface. Minor changes that lead to significant effects is known to occur in physical systems that are undergoing phase transitions (for example, where a solid changes into a liquid). The Ising model, for example, undergoes a phase transition from an ordered to disordered state once a particular temperature is reached. Cocchi et al propose that the dynamic system in the brain works in a way similar to the Isling model, with very small changes in linoleic acid concentration being associated with mental health disorders such as depression.
BMC Microbiology: New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM): a worldwide threat to public health
Another review article of note this month is from BMC Microbiology Associate Editor Asad Khan and colleagues, discussing the major worldwide concern about the emergence of carbapenemase producing bacteria, in particular New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM-1). NDM-1 is a metallo-beta-lactamase enzyme that is structurally dissimilar to other beta-lactamase enzymes. It was first identified in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from a Swedish patient who had returned from India with a urinary tract infection in 2009. It has become more prevalent in the community and in hospital settings and its markers have been identified in almost all members of the enterobacteriacae family. Khan et al provide a comprehensive view of the structural differences among NDM-1 variants, which are a driving force behind their spread across the globe. Khan also discusses his insights on the emergence of NDM-1 and its effect on bacterial antibiotic resistance in this blog post.
BMC Evolutionary Biology: Image of the month
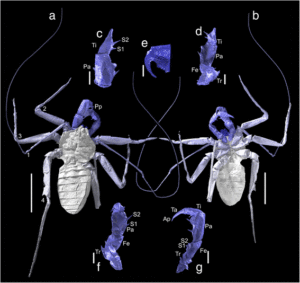
Research published in BMC Evolutionary Biology investigated the phylogeny of fossil whip spiders. The full article can be read here.
For more BMC-series research:
![]() Follow @BMC_series
Follow @BMC_series
![]() Watch our YouTube channel
Watch our YouTube channel
![]() Browse our list of journals
Browse our list of journals
![]() Subscribe to updates from our blog
Subscribe to updates from our blog
Comments